Parts of Speech
English Grammar
The parts of speech explain how a word is used in a sentence.
There are eight main parts of speech (also known as word classes): nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
Most parts of speech can be divided into sub-classes. Prepositions can be divided into prepositions of time, prepositions of place etc. Nouns can be divided into proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns etc.
It is important to know that a word can sometimes be in more than one part of speech. For example with the word increase.
Increase can be a verb e.g. Prices increased
and increase can also be a noun e.g. There was an increase in the number of followers.
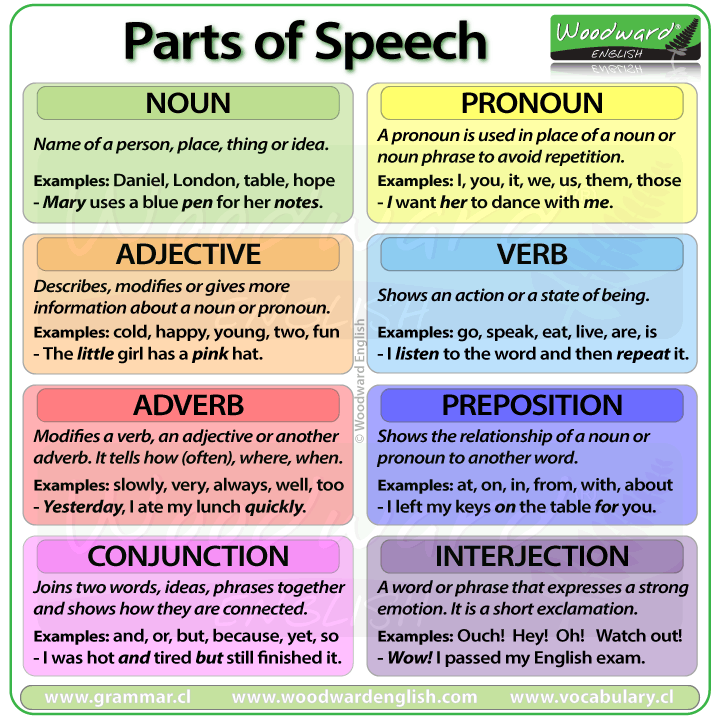
The eight main parts of speech in English are:
NOUN - (Naming word)
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing or idea.
Examples of nouns: Daniel, London, table, dog, teacher, pen, city, happiness, hope
Example sentences: Steve lives in Sydney. Mary uses pen and paper to write letters.
Learn more about the different types of nouns.
PRONOUN - (Replaces a Noun)
A pronoun is used in place of a noun or noun phrase to avoid repetition.
Examples of pronouns: I, you, we, they, he, she, it, me, us, them, him, her, this, those
Example sentences: Mary is tired. She wants to sleep. I want her to dance with me.
ADJECTIVE - (Describing word)
An adjective describes, modifies or gives more information about a noun or pronoun.
Examples: big, happy, green, young, fun, crazy, three
Example sentences: The little girl had a pink hat.
VERB - (Action Word)
A verb shows an action or state of being. A verb shows what someone or something is doing.
Examples: go, speak, run, eat, play, live, walk, have, like, are, is
Example sentences: I like Woodward English. I study their charts and play their games.
ADVERB - (Describes a verb)
An adverb describes/modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb. It tells how, where, when, how often or to what extent. Many adverbs end in -LY
Examples: slowly, quietly, very, always, never, too, well, tomorrow, here
Example sentences: I am usually busy. Yesterday, I ate my lunch quickly.
PREPOSITION - (Shows relationship)
A preposition shows the relationship of a noun or pronoun to another word. They can indicate time, place, or relationship.
Examples: at, on, in, from, with, near, between, about, under
Example sentences: I left my keys on the table for you.
CONJUNCTION - (Joining word)
A conjunction joins two words, ideas, phrases or clauses together in a sentence and shows how they are connected.
Examples: and, or, but, because, so, yet, unless, since, if.
Example sentences: I was hot and exhausted but I still finished the marathon.
INTERJECTION - (Expressive word)
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses a strong feeling or emotion. It is a short exclamation.
Examples: Ouch! Wow! Great! Help! Oh! Hey! Hi!
Example sentences: Wow! I passed my English test. Great! – Ouch! That hurt.
Summary Chart
Sometimes teachers include Articles as a ninth part of speech so we have included it here. Note, an article is a type of adjective.
ARTICLE - (Defining word)
An article is used before a noun. These are divided into definite (the) and indefinite (a, an). Articles help define nouns.
Examples: a, an, the
Example sentences: I need a dictionary. The dictionary needs to be in English.
Next activity
See our grammar notes with more details about nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections (coming soon).
English Teacher Resource

If you found this grammar guide about Parts of Speech in English useful, let others know about it.
