Present Perfect Tense
English Grammar Rules
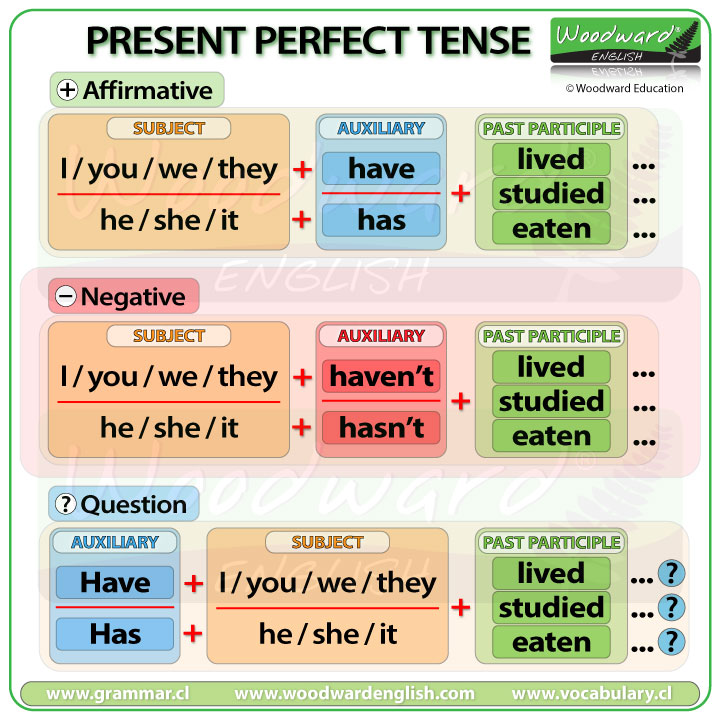
The Present Perfect Tense is formed using the following structure:
Affirmative: Subject + Have / Has + Past Participle
Negative: Subject + Haven't / Hasn't + Past Participle
Question: Have / Has + Subject + Past Participle
Affirmative Sentences
| Subject | Have | Past Participle | Rest of the Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | have | studied | for the exam. |
| You | have | bought | a new computer. |
| He | has | eaten | my chocolate. |
| She | has | written | an e-mail. |
| It | has | been | cold this month. |
| We | have | won | the championship. |
| You | have | tried | to learn a lot. |
| They | have | forgotten | my birthday. |
Contractions
The contracted form of the perfect tense is quite common:
| Have | Contraction | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| I have | I've | I've spent all my money. |
| You have | You've | You've worn that dress before. |
| He has | He's | He's slept all morning. |
| She has | She's | She's lost her purse. |
| It has | It's | It's fallen off the wall. |
| We have | We've | We've chosen you for the job. |
| You have | You've | You've begun to annoy me. |
| They have | They've | They've drunk too much. |
We use contractions a lot when we are speaking.
Negative Sentences
The contraction of the perfect tense in negative form is:
Have not = Haven't
Has not = Hasn't
| Subject | Have | Past Participle | Rest of the Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | haven't | studied | for the exam. |
| You | haven't | bought | a new computer. |
| He | hasn't | eaten | my chocolate. |
| She | hasn't | written | an e-mail. |
| It | hasn't | been | cold this month. |
| We | haven't | won | the championship. |
| You | haven't | tried | to learn a lot. |
| They | haven't | forgotten | my birthday. |
Questions
| Have | Subject | Past Participle | Rest of the Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Have | I | been | chosen for the team? |
| Have | you | bought | a new car? |
| Has | he | eaten | my sandwich? |
| Has | she | written | the letter? |
| Has | it | started | on time? |
| Have | we | won | a trophy? |
| Have | you | kept | my secret? |
| Have | they | driven | there? |
When do we use the Present Perfect Tense?
1. Unspecified point in the past
- I have been to Spain three times.
(At some unspecified time in the past, I went to Spain).
Compare with the simple past:
- I went to Spain three times in 2005.
(specified time in the past - the year 2005)
2. An action that occurred in the past, but has a result in the present (now)
- We can't find our luggage. Have you seen it?
(The luggage was lost in the past, do you know where it is now?)
3. Talking about general experiences (ever, never)
It usually refers to an event happening at some moment in your life.
- Has she ever tried Chilean wine before? (in her life)
- I've never eaten monkey brains before. (in my life)
4. Events that recently occurred (just)
- Do you want to go to a restaurant with me?
No, thanks. I've just eaten lunch. (I recently ate lunch.)
5. Events that have not occurred up to now (yet)
- Are Carlos and Rodrigo here? No, they haven't arrived yet. (they're still not here now)
6. Events that occurred before you expected (already)
- I've already graduated from University. (I expected to graduate at a later date.)
7. Events that began in the past and haven't changed (for, since)
- Mike has worked at Woodward for 3 years.
(Mike started working at Woodward 3 years ago and he still works there now.) - Julie has worked at Woodward since September last year.
(Julie began working at Woodward in September of last year, and that hasn't changed - she still works here now.)
Here are more details and and examples of when to use the Present Perfect Tense in English
Present Perfect Tense Summary Chart
Present Perfect Practice
Next activity
See our new notes about the Present Perfect Tense in English with more summary charts.
Check out our lessons about Past Participles and the Pronunciation of ED.
If you found this grammar guide about the Present Perfect Tense in English useful, let others know about it.
